Every first-time EV owner has an instant obvious concern of range anxiety and how long the battery would actually last on their EVs.
The battery pack of an electric vehicle is essential to its function and performance. It provides the power to move the car forward and often lasts for many miles before needing replacement.
Unfortunately, it can also be quite expensive to replace when it depletes to a point that it can no longer support the EV. Therefore, when purchasing an EV, it’s important to understand the quality of the battery pack as well as what kind of warranty comes with it for peace of mind.
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) has been greatly accelerated on both sides of the Atlantic. In the UK, a ban on the sale of new petrol and diesel cars by 2030 has been proposed, while in the US, it is expected that half of all new automobile sales will be electric by 2030.
The urgent boom in EV popularity demonstrates a strong commitment to greener transport options as well as a desire for society to become more sustainable. People are moving away from traditional sources of fuel towards EVs is an important step in creating a healthier, cleaner future.
But what happens when the EV battery pack is no longer fit for use on the vehicle?
Leading EV makers are investing in research and development to extend the lifespan of EV battery packs. Tesla is focusing on battery innovation, Nissan has developed a new type of battery chemistry, BMW has an intelligent charging system, and Volkswagen has rolled out its newer battery technology which uses hardware and software solutions. These efforts are aimed at making electric vehicles more reliable, affordable, and sustainable.
Let’s dig deeper to find out more about what happens when batteries are dying!
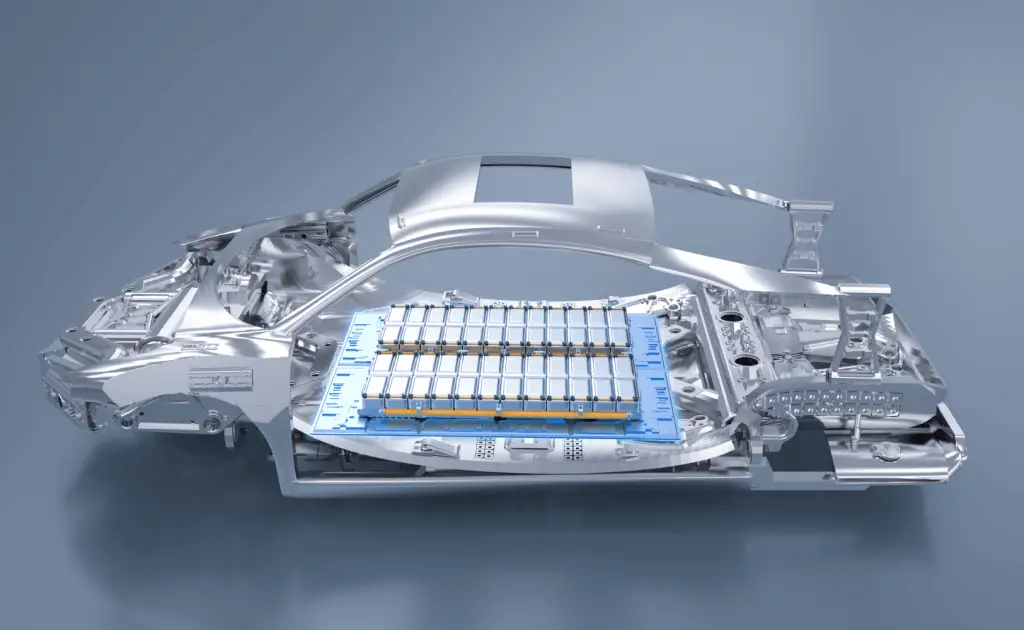

Table of Contents
What Happens to Electric Car Batteries at the End of Their Life?
Electric Vehicles (EVs) are gaining traction in the automobile industry due to their environmentally conscious design and performance. However, one of the key components of EVs – the batteries – can become a source of concern for drivers when it comes time for disposal.
Where do used EV batteries go after they’ve been retired from service?
The answer is complex and depends on the battery’s condition. Generally speaking, usable used EV batteries can be repurposed and reused in other applications.
Recycling used EV batteries to harvest materials is also an option, but it must be done with care to ensure that toxins are not released into the environment.
A combination of these two approaches — repurposing and recycling — is how most used EV batteries will find their new purpose after being retired from service.
Repurposing & Recycling EV Batteries
Repurposing used EV batteries involves refurbishing them to add more life or using them in different applications such as energy storage systems for solar panels or wind turbines, powering smaller machines like drones and robots, or connecting multiple cells together.
Slightly depleted EV batteries can still be used in applications that do not require a high level of performance. For example, they can be connected together and used to power drones or robots with slightly lower capacity or stored energy from solar panels or wind turbines with reduced efficiency.
Buying used battery packs with slightly depleted cells may still offer benefits if the buyer is willing to accept lower performance requirements.
They can also be repurposed as an energy storage system for homeowners who want to store excess energy during peak times and provide supplemental power during off-peak hours.
Repurposing Used EV Batteries
Repurposing used EV batteries involves refurbishing them to add more life or use them in different applications. This process can involve connecting multiple cells or using a single cell to power smaller machines such as drones or robots.
In some cases, old EV batteries can also be used as an energy storage system for solar panels or wind turbines, allowing homeowners to store excess energy generated by these sources during peak times and provide supplemental energy during off-peak hours.
Not all used EV battery cells have enough life remaining to make repurposing feasible. However, even with slightly depleted cells, there may still be benefits for buyers who are willing to accept lower performance requirements for their application (e.g., shorter flight times for drones).
Recycling Used EV Batteries
Recycling for material extraction is another option for dealing with drained EV batteries depending on the age and type of material contained within them.
Cobalt, nickel, and lithium are some of the materials commonly found in lithium-ion batteries which can be recycled if extracted properly. These metals have a wide range of uses in electronic components, medical technology, aerospace equipment, military applications, etc.
Moreover, recycling these metals reduces their need to be mined from natural deposits which further helps protect our environment.
Unfortunately, extracting these metals requires special handling due to toxicity concerns, so any recycling program undertaken must follow safety regulations set forth by local governments. Many leading companies and startups are researching ways to better mitigate any potential hazards associated with extracting these materials while still maximizing economic benefits.
Overall recycling used EV batteries is a valuable way that communities can generate revenue while also reducing waste in landfills. By combining this approach with repurposing viable battery packs we can keep our environment healthy while making sure everyone gets maximum value out of our electric vehicles.
How Does EV Battery Pack Works?
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular due to their efficiency and environmental friendliness. But how do these vehicles actually work?
At the heart of every electric vehicle is its battery pack, or energy storage system. The battery pack powers the motor and other electrical systems of the car.
Let’s take a look at what makes up an EV battery pack and how it works:
- An EV battery pack consists of one or more modules connected in parallel or series with each other.
- A module is a collection of cells in which each cell contains two electrodes, separated by an electrolyte solution.
- The electrodes are made from a variety of materials, including nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), lithium-ion (Li-ion), and lead acid.
- Cells are linked together to form modules which are in turn connected to form a single large battery pack.
- The role of the battery pack is to store energy from regenerative braking, as well as from charging from an external power source such as a wall charger or power grid connection point.
When the driver presses the accelerator pedal, the stored energy is used to run the motor, thereby propelling the vehicle forward. When the driver brakes, some of this energy is discharged back into the battery pack via a process called regenerative braking or ‘regen’ for short.
This helps to extend the vehicular range by reducing energy losses during deceleration and allows drivers to recharge their batteries as they drive around town without having to plug in at regular intervals.
How Does Charging Affect Battery?
Battery charging is an important part of owning a smartphone, laptop, or any other device that runs on rechargeable batteries. When you charge any battery, the chemical reactions within the battery cause it to heat up. If the battery gets too hot, it can damage the cell and reduce its lifespan.
The same thing goes for EVs. This is why it’s important to use the correct power charger and not overcharge your vehicle. Charging an electric vehicle’s battery is a fundamental part of EV ownership.
When done properly, charging an EV battery can extend its life and provide reliable performance over time. However, there are risks associated with charging an EV battery that must be taken into account. Overcharging can cause irreparable damage to the cells in the battery, while undercharging may not sufficiently charge the battery and lead to a decreased range or no power at all.
You might think that charging your Tesla on a Supercharger network can be a convenient option, but it can be detrimental to the battery’s lifespan. These high-powered chargers can degrade lithium-ion batteries at a much quicker rate than lower-powered options.
To ensure you get the most out of your electric car’s battery pack, avoid unnecessary fast charging – only use it when necessary. Additionally, try not to charge your car’s battery fully or let it discharge entirely – aim for a charge level between 85-90% as per experts.
How Long Does EV Batteries Last?
Electric vehicles have become increasingly popular due to the improved reliability and durability of their batteries. Most EV batteries are designed to retain their full charging-discharging capacity for up to 200,000 miles, and manufacturers are so confident in their battery life that they often offer extended warranties of eight years or 100,000 miles. This means you can count on your electric car’s battery to last a long time.
Graeme Cooper, a leader in the field of electric vehicle (EV) technology from National Grid, is confident that batteries will outlive the cars they are used in. He notes that today, EV batteries have an estimated life expectancy of 15-20 years within the car and can have a second life beyond it as well.
As research and development continue on this type of technology, we can expect to see batteries lasting even longer and becoming more affordable, smaller, and lighter in weight.
Electric car batteries typically can last the age of the vehicle for roughly 10-15 years depending on usage and charging habits for most EVs. Proper maintenance and careful driving can help extend the lifespan of a battery even further.
What Happens When EV Battery Cannot Power Vehicles?
When an electric car battery no longer powers a car reliably and quickly, it is typically recycled or repurposed. Many companies offer recycling services that allow you to safely dispose of your old EV batteries, helping to reduce the environmental impact of EVs.
Electric car batteries have a unique and innovative second life, even when they begin to lose their capacity to power a vehicle over a distance. With electric vehicle (EV) technology becoming increasingly accessible, battery packs that are no longer fit for onboard use can still be recycled efficiently and re-purposed for other energy applications.
As soon as an EV battery starts to show declines in performance dipping below the threshold of 70%, it’s ready to enter its ‘second life.’
This second life provides electric car batteries with many additional use cases such as energy storage for homeowners or businesses, powering remote infrastructure and villages, powering industrial equipment such as robots, or repurposing the cells into new packs.
If a battery still has life remaining, it can be repurposed by refurbishing or connecting multiple cells together to power smaller devices such as drones or robots, and they can also be used as an energy storage system for homeowners.
How Leading EV Makers Are Handling Used EV Batteries?
Electric vehicles (EVs) have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their environmental benefits. But one of the major drawbacks is that EVs suffer from battery packs that have a limited lifespan and can eventually die when used over an extended period of time.
Most electric vehicles (EVs) on the market today come with battery warranties that offer excellent protection for the owner. For example, Tesla offers an eight-year and 150,000-mile warranty on their cars – a great guarantee of quality.
Not only does this warranty cover the complete failure of the battery pack, but it also covers any serious degradation over time. While lithium-ion batteries naturally lose a small amount of capacity with each charge cycle, an EVs driving range should not suffer from this reduction if the battery is well looked after and maintained according to manufacturer guidelines.
The assurance offered by such warranties gives EV owners added peace of mind and security knowing they have comprehensive coverage of their car’s battery.
Here’s how some leading electric car makers are addressing this issue and tackling dying battery packs:
- Tesla has been at the forefront of battery innovation, introducing advanced technologies that are designed to maximize battery life. The company has invested heavily in research and development to develop more efficient batteries and deliver longer-lasting performance.
- Nissan has developed a new type of battery chemistry that is designed to extend the lifetime of the vehicle’s battery pack. The company claims that its technology can deliver up to two times greater energy density than traditional lithium-ion technologies, enabling a longer range on a single charge.
- BMW has introduced an intelligent charging system that optimizes charging times and helps reduce the overall wear and tear on electric car batteries. The system is designed to accurately measure the capacity of each cell to ensure the most efficient charging process possible.
- Volkswagen of America and Audi are joining forces to ensure that the increasing numbers of electric vehicles (EVs) in their portfolio have a proper, environmentally-friendly afterlife. In an effort to encourage sustainability, the two brands have joined forces with Redwood Materials, a battery recycling startup, to recover and reuse old battery packs from their rapidly expanding fleet of EVs.
What To Expect In the Future?
The biggest challenge with EV batteries is maximizing their range while keeping them lightweight and affordable enough for practical use in daily life – something that many manufacturers are still working on achieving today.
As EVs become more commonplace around us, we can expect further advances in battery technology that will make them even more efficient and cost-effective in years to come.
Overall, leading EV makers as well as some startups like Li-Cycle, Redwood Materials, etc. are investing in research, development, and technology to tackle dying battery packs for electric cars. These efforts are vital for helping electric vehicles become more reliable, affordable, and sustainable solutions for tomorrow’s transportation needs.
Electric vehicles are shaking up the automotive industry and ushering in a new era of clean transportation. Batteries are the most important part of this revolution, but they also come with significant costs and bring about geopolitical, industrial, and environmental changes.
It is predicted that EV sales will account for over half of all passenger car sales in the US by 2030, and the global battery market could require 90 more facilities the size of Tesla’s Gigafactory to be built over the next decade.
According to estimates from the U.S. Department of Energy, modern electric car batteries are expected to have a life span of up to 15 years when used in mild climates and 8-12 years when used in more extreme conditions. So regardless of how often you drive your EV, it should last for many years with proper care and maintenance.
Bottomline
Repurposing used EV batteries involves refurbishing them to add more life or use them in different applications such as connecting multiple cells together, powering small drones or robots, and storing energy from solar panels or wind turbines.
Not all used EV battery cells have enough life remaining to be repurposed, but buyers may find value in batteries with slight depletion for lower-performance applications.
For the foreseeable future, electric cars are likely to remain powered by the same type of battery technology that we use today. While it is certainly possible that new, more efficient, and powerful fuel sources could be developed in the future, nothing indicates that these advances will be coming any time soon. Until then, a rechargeable lithium-ion battery is what keeps our electric vehicles running.
As with most any technology, Electric Vehicle (EV) batteries will undoubtedly require replacing down the road. However, they are expected to last quite some time before that need arises.
In fact, the modern EV battery pack should remain effective and reliable without any problems for at least the first 10 years of use, perhaps even longer. By the time these vehicles need new batteries, manufacturing, and material costs will likely have decreased significantly from today’s levels.