Self-driving is currently the buzzword in the automobile industry. With vehicles undergoing electrification, the overall vehicular architecture is moving towards software more than ever before. This has prompted many automakers to add driver-assist systems as well, which, with further development, can move towards autonomous systems. But automakers aren’t the only ones cashing in on such systems. There are third-party companies with after-market products that allow you to have driver-assist systems in your vehicle.
How To Make Your Car Drive Itself
Comma.ai – An Overview
One such company is Comma.ai, which launched their Comma Two product last year. George Hotz, an American hacker, founded Comma.ai in September 2015. He is best known for developing exploits that targeted Apple’s iOS and for reverse-engineering Sony’s PlayStation 3. The idea behind Comma.ai was to develop a semi-automated system that would improve cars’ visual perception and electromechanical motor control. Hotz named this system Open Pilot and intended it to replace OEM advanced driver-assist systems.

Of course, the company didn’t have the best of starts. Comma.ai first tested Open Pilot in California but got a cease-and-desist letter from the Department of Motor Vehicles. They accused Comma.ai of testing a self-driving car without a license. The company tried to sell the software through a shippable device called Comma One, but it hit similar roadblocks. The company then open-sourced the software on GitHub.
Since then, over 1,500 users have accessed the software through GitHub, and as of March this year, they have racked up 40 million miles (64 million km) of driving. Around half of those have been driven autonomously. There have been a number of feature additions too, like automatic lane change and support for older models of certain automakers.
Comma Two
Comma.ai has developed its latest product on the back of these self-driven miles. It first began as Eon Devkit, which can automatically recognize car models by analyzing CAN network traffic. The companion devices track the vehicle’s RPM, MPG, cornering G-force, battery life, etc. The Eon Devkit evolved into Comma Two, which includes a few more features.
The Comma Two uses a custom fan-based hardware cooling solution, and also contains facial recognition, which slows down the vehicle if the driver is distracted. After all, Comma Two is currently at Level 2 of autonomous driving. To be able to take your eyes off the road, you need at least Level 4. It also uses an RGB sensor that helps it work at nighttime.
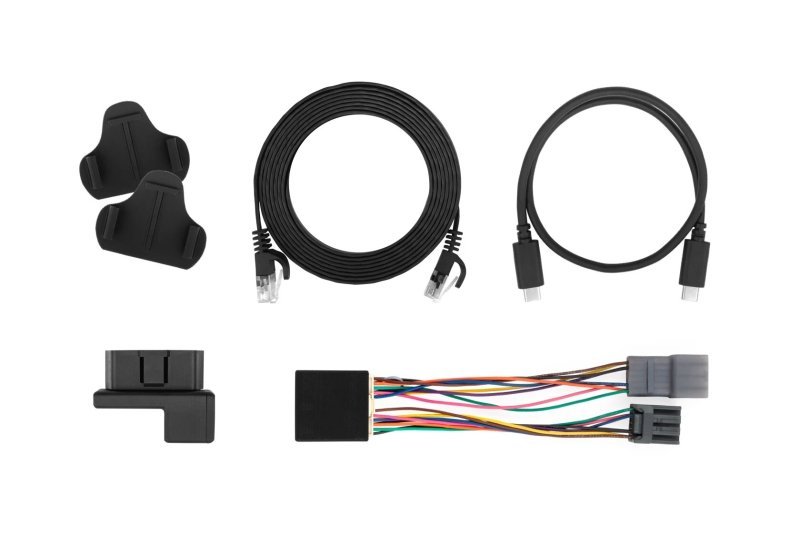
Other highlights include front and back cameras, as well as a fourth CAN bus to connect the OBD-II port and a low-power mode that automatically shuts off the Comma Two after three days to save the car battery. Users could elect to spring for Comma Prime, a $24 per month service that enables remote access (via T-Mobile) from anywhere and online storage of 14 days’ worth of drive data (compared with the standard three days).
Comma AI Supported Cars
At the moment, Open Pilot supports a selected roster of vehicles. A number of Honda models such as Accord, Civic, Odyssey, and Toyota vehicles such as Avalon, Camry, Corolla, Highlander, Prius, and Sienna make the list. Other models include Hyundai Elantra and Genesis, Jeep Grand Cherokee, Lexus RX Hybrid, Cadillac ATS, Chevrolet Malibu, and Acura ILX.

Obviously, Open Pilot isn’t capable of fully autonomous driving in all conditions. At the moment, it can manage lane-centering and maintain a safe distance while following other vehicles. It does however give a ‘smooth sailing’ experience while driving. It is smart enough to stay in one lane even if the markings are unclear or absent.
Backend Development and Future Scope
Behind the equation of Open Pilot, there is a simulation environment called Small Offset Simulator. This helps in simulating deviations, which is something you cannot do in the real world. It uses a technique called projected geometry and generated adversarial networks (GANs). GANs are basically two-part AI models comprising generators that synthesize data samples and discriminators that attempt to distinguish between the synthesized samples and real data.
At the moment, it is similar to environments that companies like Uber, Waymo, GM use. Going forward, Comma.ai plans to release new hardware on a roughly yearly cadence — Hotz believes its business model of selling devices at profit and eating the cost of software development is sustainable. (Comma.ai has raised $8.1 million in venture capital to date across two funding rounds, the most recent of which closed in April 2018.) As for OpenPilot, achieving a better end-to-end driving experience remains an acute area of focus for the engineering team.
Our Opinion
This kind of third-party product is something we don’t see in use in normal scenarios. The main reason behind that is the automakers not supporting this kind of after-market modification. After all, you need to plug in a new harness and a small device into your vehicle that takes over driver-assist duties from the original system. Furthermore, there is some competition brewing for autonomous driving as well, such as Mobileye.
George Hotz, however, is unfazed by the competition. He says:
Mobileye is the Windows [of autonomous driving] that’s going to do Microsoft-style business development deals with big companies, Tesla’s the Mac that’s going to ship sexy hardware to consumers, and we’re the Linux.



