There has been a lot of discussion regarding electric vehicles in the market currently. Electric vehicles have started taking a chunk out of the customer base for the past few years. One of the questions being asked is what kind of transmission do electric vehicles have. Are electric cars automatic or manual? Do they have gears? So here’s an article that talks in detail about this topic – Are Electric Cars Automatic Or Manual?
Many people across the globe have had reservations about electric vehicles. This is mainly because of a lack of awareness regarding the actual working of electric cars. While there may not be a major difference between driving a combustion vehicle and an electric vehicle, their systems differ a lot. This mainly includes the transmission system.
Table of Contents
Are All Electric Cars Automatic?
The answer is no.
This is a myth in the automotive industry that every electric car has an automatic transmission. This is mainly because very few manual electric vehicles are seen in the industry. In fact, most people don’t even know that manual transmission exists in electric vehicles. Most of the mainstream EV manufacturers have a single gear ratio, so the question of having a transmission does not arise.
Do Electric Cars Have Engines?
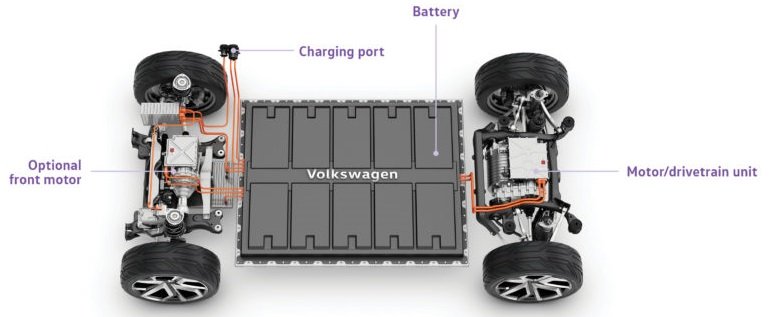
This is quite a basic question, and most people know that the answer is no. The powertrain of an electric car consists of a battery that supplies energy. There is an electric motor that uses the energy from the battery to drive the axles. So the engine-transmission system in a combustion vehicle is replaced by a battery-motor combination here.
Now that we know the basic powertrain system in an electric car, let’s understand the difference in the working of motors and engines.
Engines vs Motors
Internal combustion (IC) engines are normally accompanied by a manual transmission system. This is because IC engines can generate efficient power only across a limited range of RPM (revolutions per minute of the engine’s crankshaft). Normally, the torque produced is highest at lower gears, and it goes on decreasing gradually. By selecting proper gear ratios, the transmission system can transmit the adequate amount of power and torque from the engine to the axles across a wide range of RPM.
As opposed to this, electric motors can function over a much wider range of RPM. They can produce a near-constant amount of torque across the range of RPM, thus eliminating the need for having a multi-gear transmission system. Secondly, IC engines have to build up torque by revving, which is not needed in motors. This is because electric motors can generate torque instantly, which allows electric cars to get a much better launch than combustion vehicles.
Do Electric Cars Have Transmissions?
Electric cars usually have just a single gear and don’t have traditional transmissions like internal combustion engines. This is because a traditional transmission system with multiple gears might cause inefficiencies. Hence, it is common to see automatic electric vehicles.
One of the major differences between engines and motors is that engines cannot function at all outside the given range of RPM. This means that a higher gear will work only for a higher RPM, and it will struggle to give power to the wheels at a lower RPM. Let’s understand this through a basic example.
Need of gearbox in automobile
Consider that we have two cars – one combustion vehicle and one electric vehicle. Both have a top speed of 225 kph (62.5 metres/sec). For a tire of diameter 0.68 m, the circumference comes out to be 2.137 m. Electric motors are capable of working at 20,000 RPM, so using the standard formula (given below), the gear ratio can be calculated as 11.4.
[Gear ratio = Number of driven gear teeth/Number of driving gear teeth]

This means that if we have an electric motor that revs to 20,000 RPM with a gear ratio of 11.4, then we could drive the electric car from 0 Km/h at 0 RPM to 225 Km/h at 20,000 RPM. Thus, a single gear ratio can work for an electric motor across a wide range of RPM and still give efficient power.
In comparison, internal combustion engines have a lot of limitations. Passenger vehicles normally run at 6000 RPM, and considering the same gear ratio of 11.4, an internal combustion engine can generate a speed of just 67.5 kmph (18.75 m/s). In order to reach a speed of 225 kmph (62.5 m/s), it will need a gear ratio of 3.4.
Here lies the major problem. At a gear ratio of 3.4, to drive at a speed of 20 kmph, the required RPM will be 580, which is awfully low. Even if the engine is able to operate at this speed, it cannot generate sufficient torque to move the vehicle. This is why a combustion vehicle requires multiple gear ratios, and consequently, multi-gear transmission systems. It will use a higher gear ratio for lower speeds and a lower ratio for higher speeds.

Why Do Electric Cars Have Only One Gear?
Unlike traditional gasoline-powered cars, which rely on a complex system of gears to transmit power from the engine to the wheels, electric cars use a single-speed transmission or no transmission at all. This simplicity not only reduces the complexity and cost of the drivetrain, but also increases efficiency and reliability.
Additionally, electric motors have a wide operating range, allowing them to maintain their peak torque across a broad range of speeds, further reducing the need for multiple gears.
A multi-gear system will mean more moving parts that are in contact with each other. This, in turn, will cause inefficiencies in the system. But that does not mean that electric cars must have only one gear.
Do Electric Cars Have Gears?
The major point to be considered here is that the need for having a transmission system directly depends on the range of RPM over which the motor can work efficiently. This, in turn, depends on the voltage of the entire powertrain system. For vehicles such as Tesla, the voltage of the system is as high as 400 volts. A voltage this high is sufficient to produce a large amount of torque over 12,000 RPM. At the same time, a system of 120 volts can produce usable torque over just 4,500 RPM. That is why an electric vehicle with a lower voltage system will require a transmission system to produce torque over a high range of RPM.
Do Electric Cars Have Neutral?
Since most electric cars have an automatic transmission, the question of whether they have a neutral gets solved easily. There are three options on a switch – Drive, Neutral and Reverse. The appropriate option can be selected for the required situation.
Do Electric Cars Have A Clutch?
The clutch pedal obviously won’t make it to the manual electric vehicles. And they shouldn’t, because they are not required. It will only add to the complexity of the system. But overall, a manual transmission electric vehicle is a possibility.
Advantages of Adding Multi-Gear Transmission for Electric Cars
Electric vehicles with multi-gear transmission have slowly started coming onto the market. The most recent and notable addition to this is the Porsche Taycan. The electric addition to Porsche’s lineup has a two-speed transmission system.
The advantages of having a multi-gear system are similar to those in combustion vehicles. Acceleration at lower speeds improves a lot. The efficiency at higher velocity increases by lowering the rotating speed of the power source. In other words, the ratio distribution of the two-speed transmission will not only help the range but also make it fast.
Porsche’s gearbox consists of a single planetary gearset and two clutches. The clutches can either handle ratio swap or decouple the rear motor altogether. This allows the car to be run on the front axle only. The step-up of the gear ratio is high, with the second ratio being around half of the first. The shift from first gear to the second happens roughly around 50 mph (80.5 kph).
This two-gear setup should help Porsche in the highway driving scenarios. The constant high-speed running is supposed to be electric cars’ Kryptonite. But the higher gear will help the Taycan to improve range.
Are Electric Cars Manual?
This is a very interesting topic. In theory, an automatic transmission will give you more efficient acceleration. As you go on adding multiple gears, the efficiency of the powertrain will go on decreasing. But that does not mean manual electric cars do not exist. Answering the above question requires the consideration of several factors, and it has less of a technical basis and more of an emotional one.
Manual transmission, in any type of vehicle, is something that drivers find really enjoyable. It is something that makes a drive memorable for every driver. Any person who loves driving knows the joy of shifting as you drive along a beautiful road, getting in sync with the emotion between you and your car, and maximizing the potential of your vehicle according to the road situation.
It brings in a combination of thrill and passion, it is what makes you fall in love with driving and never tires you out even after a significantly long drive. And this is exactly the emotion that many automakers want to capture. Even in today’s age, where automatic transmission is ruling the roost, some companies have stuck to the manual transmission option. And this has more to do with emotion than logic.
And this applies to electric vehicles as well. Yes, you may not really require a manual stick shift in an electric vehicle. Heck, you won’t even require extra gear most of the time. But it is the need of capturing that emotion that makes this discussion necessary.
The question of whether electric vehicles can have manual transmission can be answered in two ways – whether it is possible and whether it is logical.
Can Electric Cars Be Manual?
The answer is yes. From a pure perspective of whether you can do it, the answer is always going to be yes. All you have to do is replace the engine in a combustion vehicle with an electric motor. It is that simple. Yes, you may not be able to use the transmission system as it is, and yes, it might take a bit of modification, but it can be done. While the manual transmission in a combustion vehicle helps to supply adequate power, a manual transmission in an electric vehicle helps to control the power being sent. And to ensure that this discussion does not remain solely theoretical, we have some real-life examples of manual transmission electric vehicles.
EV West – Electrifying Your Old Classics

Michael Bream is the founder and CEO of EV West, which provides custom-made and off-the-shelf products aimed at helping people convert their classic Volkswagen and Porsche cars to electric propulsion. The aim is to make this transition as seamless as possible, which means swapping out as fewer parts as possible. And for these classics, it means keeping the original manual transmissions.
Of course, they do not keep the manual transmission as it is. The extra gears are removed, and they keep a two-speed transmission system, along with the stick shift in place. It is also named as simple as “Low Gear” and “High Gear”. And it is just as simple to explain to the customers. Stick to ‘Low’ in the city, and once you hit the highway, move to ‘High’. Even the reverse gear is removed from the shift, as there is a button on the dashboard which inverts the power, and spins the motor into reverse. But the traditional clutch pedal and stick shift remain, and customers can drive these electrified classics just the way they would drive any manual transmission car.
And this brings us to one of the most talked-about points in electric vehicles in the past year – The Ford Mustang.
An All-Electric Ford Mustang – A Futuristic Move or A Cardinal Sin?

The Ford Mustang always has a special place in the heart of any combustion vehicle lover. The Mustang has always been the go-to vehicle when it comes to talking about emotions. And why shouldn’t it? After all, the very sound of its engine is so pure, that it is enough to drive any person crazy. But then, last November, an announcement was made, one that filled all ‘petrolheads’ with rage. It was considered sacrilegious, as one of their most loved cars underwent electrification.
During last year’s SEMA show, Ford unveiled their one-off all-electric car, the Mustang Lithium. The Specialty Equipment Market Association, or better known as SEMA, hosts a show every year. It is a platform for hot rodders and customizers to show off interesting projects. These projects push the boundaries of what people can do with aftermarket parts. Many of the automakers use this as a stage to unveil their one-off concept vehicles.
Ford teamed up with Webasto to produce an electric concept vehicle, and they based it on the Mustang. With 900 horsepower and 1355 N-m of torque, even this Mustang is a beast, albeit with a battery. And just to make things fun, Ford gave the Mustang Lithium a 6-speed manual transmission. While this car may not find itself in the hands of the general public, it showed that even OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) like Ford have the thought process of having a manual transmission electric vehicle.
Tesla’s Transmission Problems

When Tesla launched the Roadster back in 2008, they were dealing with a unique issue. The first iteration of the transmission system had some serious transmission issues, which were later seen in the Model S as well. The components of the drivetrain would give away too early into the vehicle’s life. In order to solve these durability issues, Tesla had come up with a new two-speed transmission system. The first batch of the Roadster, dubbed ‘P1’, contained this two-speed gearbox. The problem was that this drivetrain severely impacted the Roadster’s acceleration. It would take 5.7 seconds to go from 0 to 60 mph (96.5 kph). This was quite slow, even by 2008 standards. And Tesla had promised a sub-4 second timing.
Essentially, having a two-gear transmission for a 366-volt electrical system was affecting the performance. Tesla then decided to go back to the drawing board. A new single-gear system was designed, which would be able to provide more power to the axles. This new transmission system had advanced cooling capabilities to handle the extra power output. It also had a more robust system to handle the extra torque. Thus, it is not always necessary to have a multi-gear system. If your electrical system has a high voltage, then your car will have the capability to deliver across a wider range of RPM.
So, we know that it is possible to have a manual electric vehicle. Now, to answer the second question – is it logical to have a manual transmission electric vehicle?
Is It Logical To Have Manual Transmission In Electric Vehicles?
Quite frankly, the answer is no. And the simplest explanation for that is that you will rarely find an electric vehicle that actually requires multiple gears. The need for a multi-gear system arises when a single-gear ratio cannot cover a wide range of RPM, as in most internal combustion engines. But for motors that are powered by high voltages such as 400 volts or more, a multi-gear system is an unnecessary addition. It increases weight, and consequently, the cost too. For cars with lower voltage systems, you might add a second gear. But most electric vehicles, like Tesla, have an electrical system that provides sufficient torque and power for over 12,000 RPM.
So, the question of whether or not an electric vehicle should have a manual transmission gets solved easily. Yes, having a manual transmission will give you a vehicle that is fun to drive, but it is just not practical.
So there you go. An electric vehicle can have a manual transmission, and it is something that automakers have been exploring to capture the audience. But if you talk from a point-of-view of performance, then the question of “Electric Vehicles – Manual vs Automatic” will always have the latter coming out on top.



