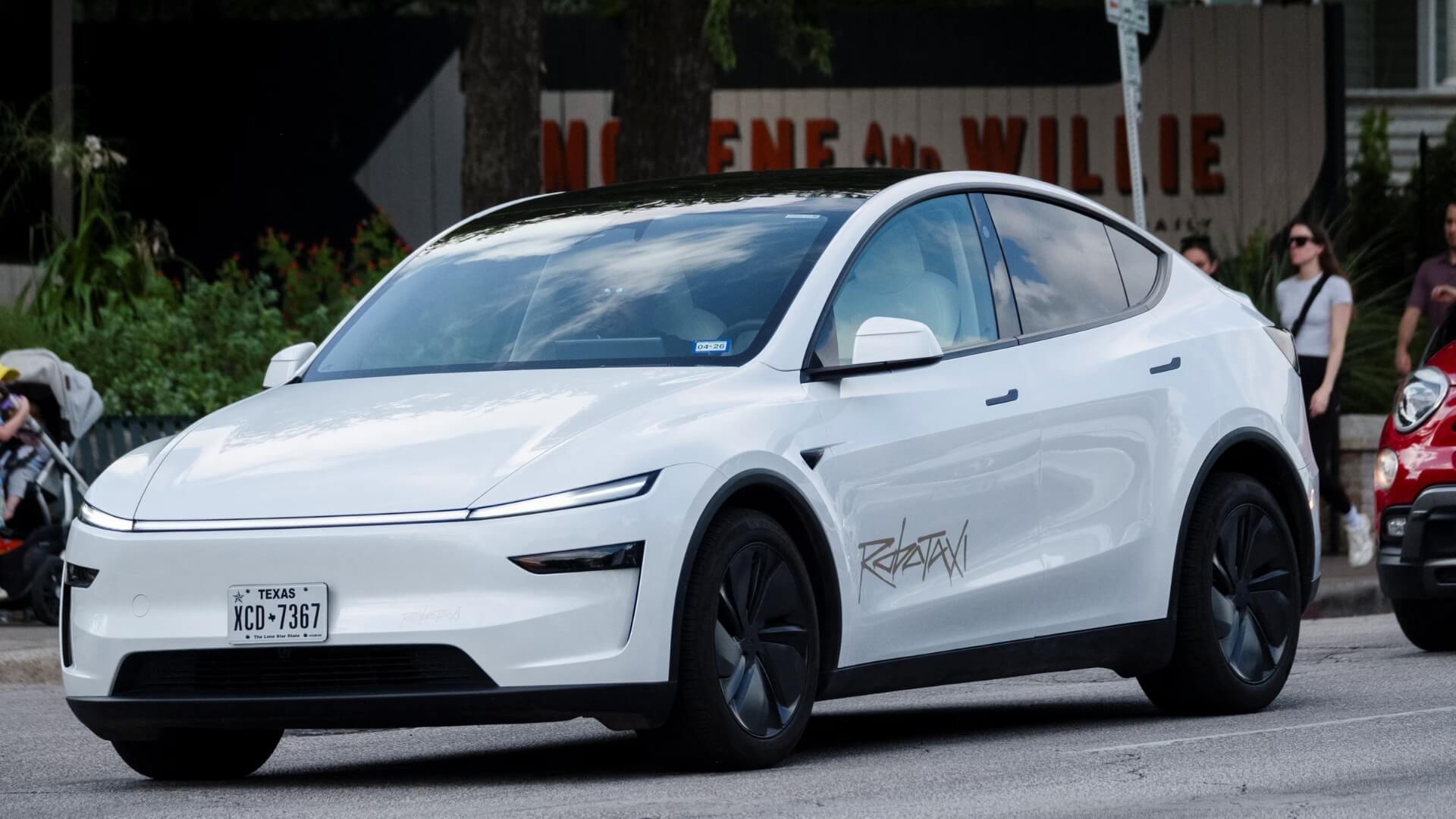
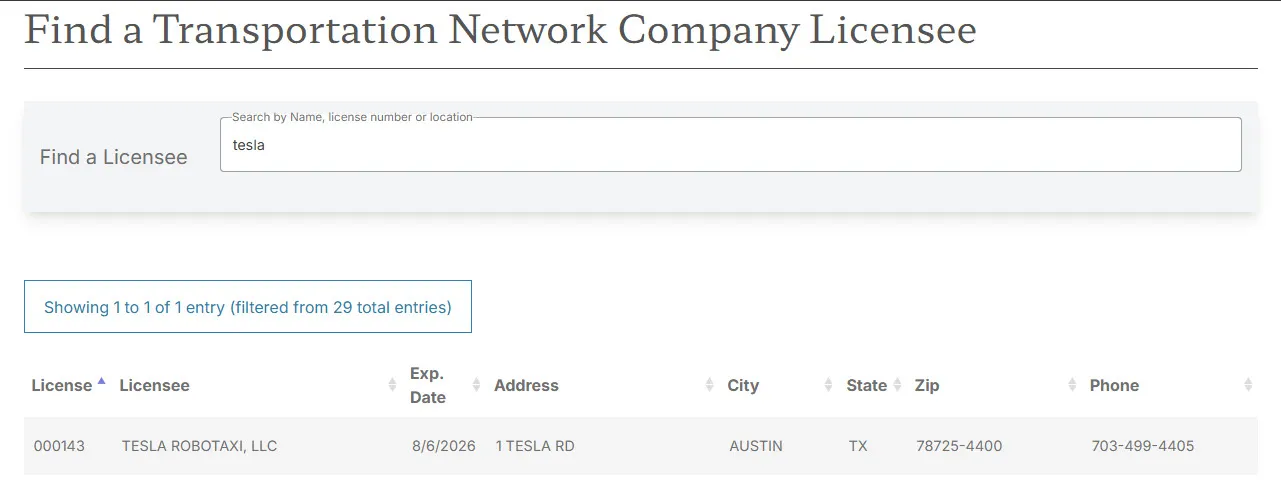
Tesla was granted permission by the state of Texas to implement its version of Robotaxi, operating without human safety drivers – the very first milestone in the autonomous vehicle aspirations. In a regulatory move, the Texas Department of Licensing and Regulation (TDLR) issued a permit to Tesla Robotaxi LLC and permitted it to operate as a licensed Transportation Network Company (TNC) until August 6, 2026.
That permission is based on a new Texas law that establishes the statewide standards by which self-driving vehicles may operate. In contrast to most of its competitors, whose authorizations remain pending human authorization, Tesla’s permit expressly permits the use of fully driverless cars.

Statewide Approval out of Austin Pilot
Tesla took the first step toward this milestone back in late June when it launched a pilot robotaxi service in Austin. The first fleet was Model Y with Tesla’s latest Full Self-Driving (FSD) software. Initially, it invited a small number of users to ride in its cars exclusively by invitation; a trained safety operator was seated in the forward passenger seat to observe performance.
Over the last few weeks, Tesla has expanded the Austin service area multiple times, adopting a gradual approach that has increased both the fleet of cars in service and the overall route zone. In that TNC permission that was issued this week, the onboard safety operator is not needed anymore, but the company has not specified yet when people in the state will be able to get fully autonomous rides.
Industry analysts say the action would provide Tesla with a commanding position in the new autonomous mobility industry, particularly in a state that has been characterized by large cities and high vehicle utilization rates.
Launch Will Be Next Month
With the announcements about the permit, the Tesla CEO, Elon Musk, revealed that the Tesla Robotaxi service will be available to the rest of the world next month. This comes after months of internal preparation, refinements to the software, and gradual scaling-up of the pilot program.
Musk has expressed the possible size of Tesla’s ride-hailing autonomous platform, claiming that by the end of 2025, the service might cover half of the U.S. population. Launching the service across the state of Texas, which is the second-largest state in the nation by both population and size, is regarded as a significant step to achieving that aim.
The firm is anticipating a huge rise in demand following the wider launch, with additional cars being introduced to satiate the ridership requirements. Whereas the original Austin program was based on a modified Model Y SUV, the company is also working toward a purpose-built robotaxi vehicle, which Musk has alluded to being released within the next year.
A New Regulatory Regime
On September 1, the new autonomous vehicle law of Texas will come into effect, which stipulates a standardized framework that will apply to all AV operators regardless of whether their vehicles are controlled by a human operator or a fully autonomous one. According to the law, companies will need to ensure that they have active insurance policies, a fully functional camera system, and rigid compliance with the traffic rules.
With the TNC permit, the activities of the company will be within this regulatory jurisdiction, with state authorities having control over safety and the quality of its services. The advocates argue that the simple, clear statewide regulations will promote innovation and preserve the confidence of the people. According to critics, however, eliminating the human safety drivers so fast would put passengers and other users of this facility at unnecessary risk.
By granting the permit, regulators have cast a vote of confidence in Tesla and assessed the company to challenge its technology to show it is prepared to handle real-world situations in large volumes. The company would have to reconcile the thrill of becoming driverless and the desire to be safe in the indirect and uncontrollable complex traffic situation.


















